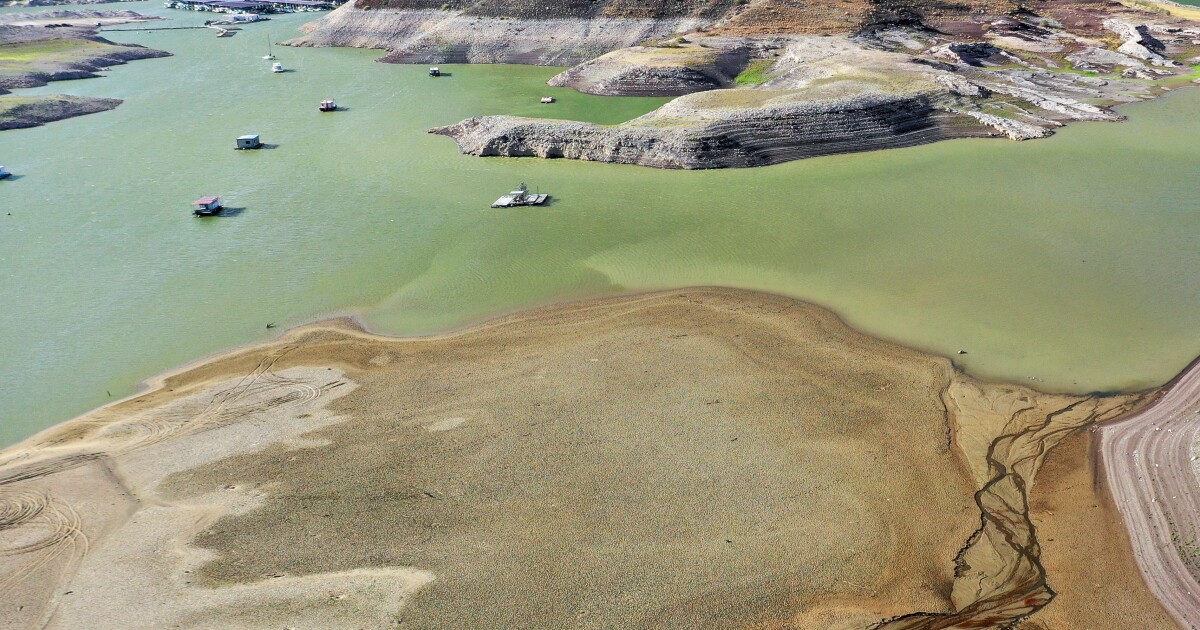
Take a period of limited rainfall. Add heat. And you have what scientists call a ‘hot drought’ – dry conditions made more intense by the evaporative power of hotter temperatures.
A new study, published in the journal Science Advances, Wednesday, finds that hot droughts have become more prevalent and severe across the western U.S. as a result of human-caused climate change.
“The frequency of compound warm and dry summers particularly in the last 20 years is unprecedented,” said Karen King, lead author of the study and an assistant professor at the University of Tennessee in Knoxville.
For much of the last 20 years, western North America has been in the grips of a megadrought that’s strained crop producers and ecosystems, city planners and water managers. Scientists believe it to be the driest period in the region in at least 1,200 years. They reached that determination, in part, by studying the rings of trees collected from thousands of sites across the Western U.S.
Soooooo, positive feedback loop.